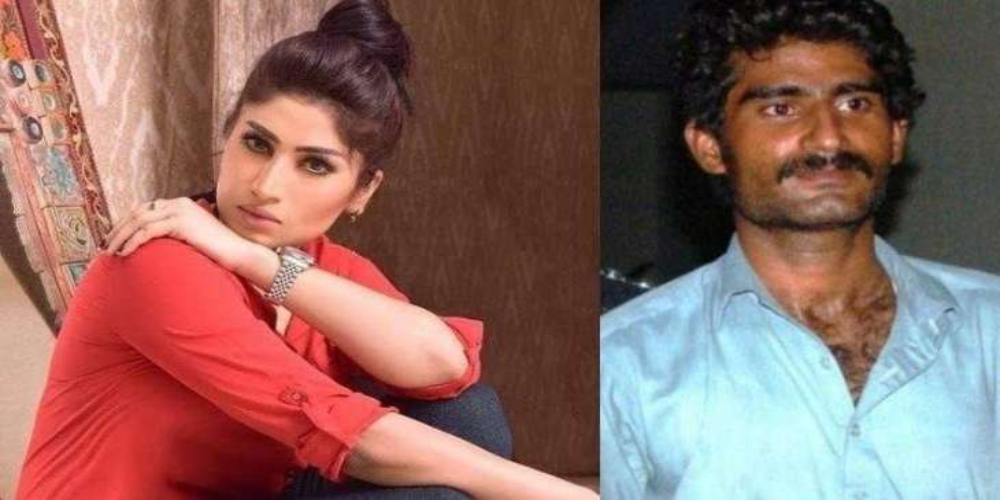
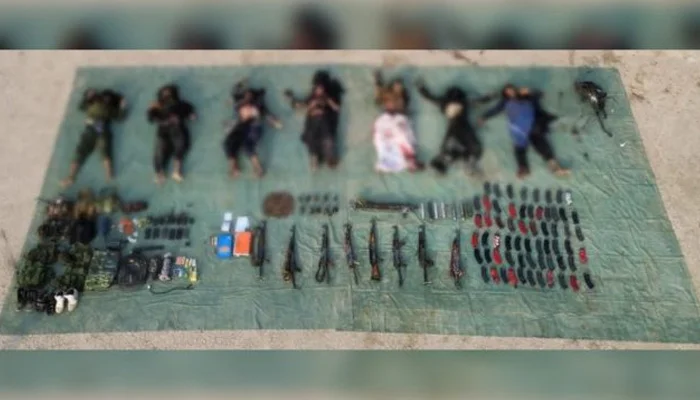
LAHORE: The Punjab government has approached the Supreme Court challenging the acquittal of slain social media celebrity and model Qandeel Baloch’s brother in her murder case.
The petition moved through Additional Prosecutor General, Khurram Khan under Article 185(3) of the Constitution and prayed the apex court to set aside the Lahore High Court’s judgment for being “sketchy, illegal” and in “contravention of the law” and that and restore the trial court’s verdict that declared him a convict.
Read more: Prime suspect in Model Qandeel Baloch murder case acquitted
A model sessions court in Multan had convicted Waseem in 2019 and sentenced him to life imprisonment under section 311 PPC after finding him guilty of killing Fouzia Azeem, known as Qandeel Baloch, said to have been murdered in the name of honour. Five other accused were acquitted of the charge leveled against them. Waseem was acquitted by the LHC earlier this month after serving less than six years in prison.
The petition filed in the SC Lahore Registry on Saturday states that the LHC had acquitted Waseem based on a “compromise” after Waseem moved an application against his conviction in the LHC.
Outlining various aspects that need to be reviewed in relevance to the case, the petition termed the LHC’s judgment “sketchy, illegal, bad in the eyes of the law” and “liable to be set aside.”
The petition argued that the high court’s judge had “failed to properly consider the settled principles about the acquittal of the accused,” and the court had “arbitrarily and erroneously” accepted Waseem’s appeal for his acquittal “without appreciating the material facts of the instant case.”
The judgment, it said, was the result of “misreading and non-reading of the material on the file.”
The petition contended that the LHC’s judgment “allowed the perpetrators of honour killings to avoid punishment by seeking forgiveness” and “essentially endorses such barbarism.” Consequently, it argued, “the eternal loophole which assumedly had been rectified by the Criminal Law Amendment (Offences in the Name or Pretext of Honour) Act, 2016, stood nullified in light of the impugned Judgment, thereby enabling regressive interpretation of the law”.
“Furthermore, due to acceptance of the aforementioned compromise, no one is in a position to pursue the case on behalf of the deceased and come forth to contest the injudicious acquittal of the accused, which disrespects the equal application of the law and undermines the general public’s confidence, faith and trust in our criminal justice system,” the petition read.
“While extending the benefit of the doubt to the accused … [the court] diminished salient features which make the prosecution case reliable and trustworthy,” the petition stated, adding that there was insubstantial use of the sufficient evidence available on record to incriminate the accused.
It added that despite a “compromise” being reached between the parties, the court “was not to blindly and impulsively act upon said compromise to acquit the accused.” Instead, the judge “ought to apply his judicial mind to the facts and circumstances of the case and proceed to convict the accused on the principles of fasad fil arz.”
The plea further contested that the principle of fasad fil arz (mischief on earth) — which is covered under Section 311 of the Pakistan Penal Code and under which Waseem was convicted — was applicable to the case as it was a case of honour killing.
Under a recent law change, perpetrators are no longer able to seek forgiveness from the victim’s family — sometimes their own family — and to have their sentences commuted.
However, whether or not murder is defined as a crime of honour is left to the judge’s discretion, meaning killers can theoretically claim a different motive and still be pardoned.
“There is no requirement under law to record evidence to ascertain the question of fasad fil arz after waiving or compounding the right of Qisas (retribution), in particular, when Section 311 PPC unfurls that the facts and circumstances of a particular case warrant the punishment of an offender under Section ibid against whom the right of Qisas has been waived or compounded,” the petition said.
The LHC judge “erroneously deciphered” that reaching a compromise before the framing of charges rendered the provision of Section 311 PPC inapplicable.
The petition argued that the judge “erroneously observed that there must be clear and qualitative evidence in order to prove the question of fasad fil arz because the only prerequisites that need to be fulfilled are the facts and circumstances of a particular case and the same does not require any evidence”.
The plea said there was sufficient evidence to secure Waseem’s conviction and that the accused had voluntarily confessed to the crime.
Read more: We should be ashamed: Fawad reacts to LHC verdict in Qandeel Baloch case
The judge, it said, “erred in holding that the offence had been compounded, thus, same entitled the accused to earn his acquittal.”
The petition said the judge acted “blindly and impulsively” on the said compromise and the subsequent acquittal of Waseem was a “sheer contravention of the relevant principles of law.”
It added that the LHC judgment on Waseem’s acquittal was based on “misinterpretation and misapplication of law and has caused a serious miscarriage of justice”, adding that it is pregnant with serious infirmities and flaws. It added that if the judgment was not set aside, the appellant would suffer irreparable loss.