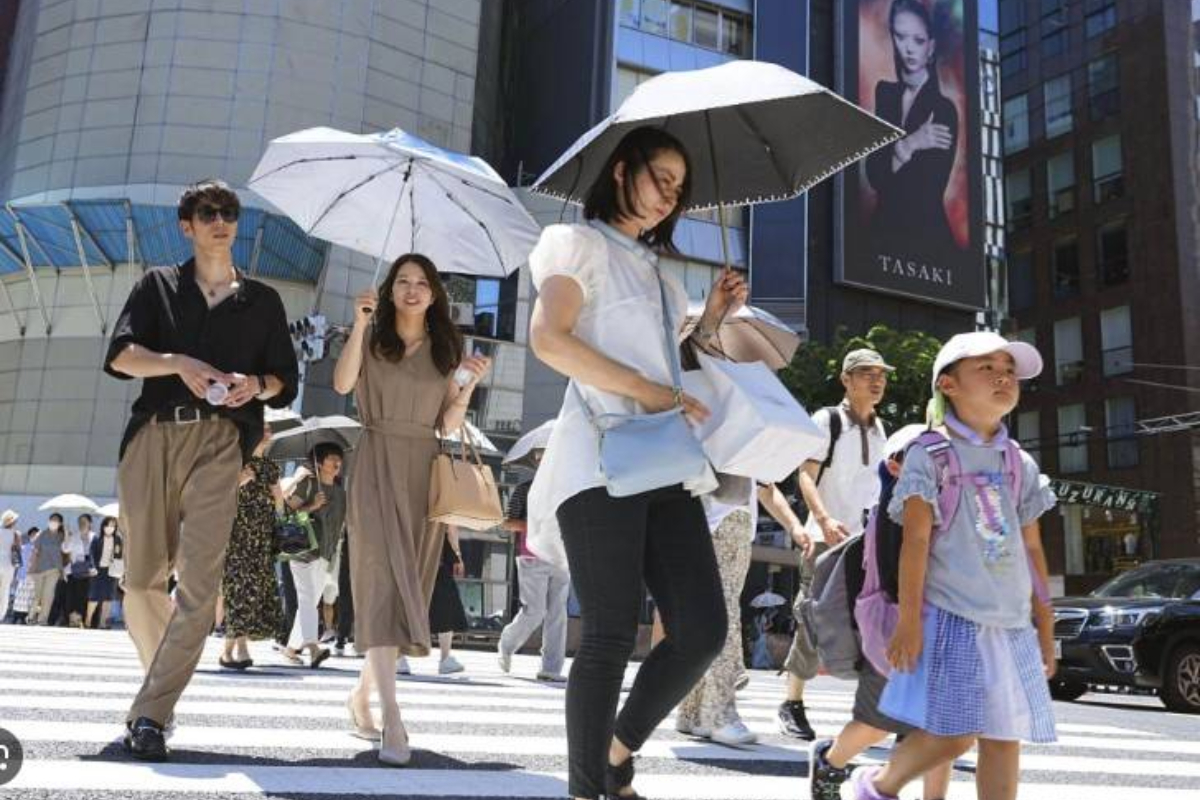
China has officially reported its hottest year since 1961, when reliable temperature monitoring began. The average national temperature in 2024 reached 10.92°C (51.66°F), marking an increase of 1.03°C compared to 2023 and solidifying 2024 as the warmest year on record.
According to the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), the four warmest years in China’s history have all occurred within the last four years, with every year in the 21st century ranking among the ten hottest on record.
Shanghai, the country’s financial hub, also experienced its hottest year since records began in 1873. The city recorded an average temperature of 18.8°C (65.8°F), surpassing all previous highs.
Rising Temperatures and Extreme Weather
The record-breaking heat reflects a troubling trend of rising temperatures across China. In 2024, the country experienced its hottest July, August, and autumn on record. Alongside the heat, extreme weather events such as stronger storms and heavier rainfall have intensified.
Devastating floods affected multiple regions, forcing thousands to evacuate and resulting in dozens of fatalities. In May, prolonged rainfall caused a highway collapse in southern China, killing at least 48 people. Typhoon Gaemi exacerbated flooding in central and southern areas, leading to widespread destruction.
Guangzhou, a major southern city, endured its longest summer ever, with temperatures remaining above 22°C (71.6°F) for 240 days, breaking the previous record of 234 days set in 1994. These persistent heatwaves have raised concerns about public health, energy consumption, and agricultural stability.