- Ghana has confirmed its first two cases of the highly infectious Marburg virus disease.
- The patients, who later died, tested positive for the virus from the southern Ashanti region.
- World Health Organization says more than 90 contacts are being monitored.
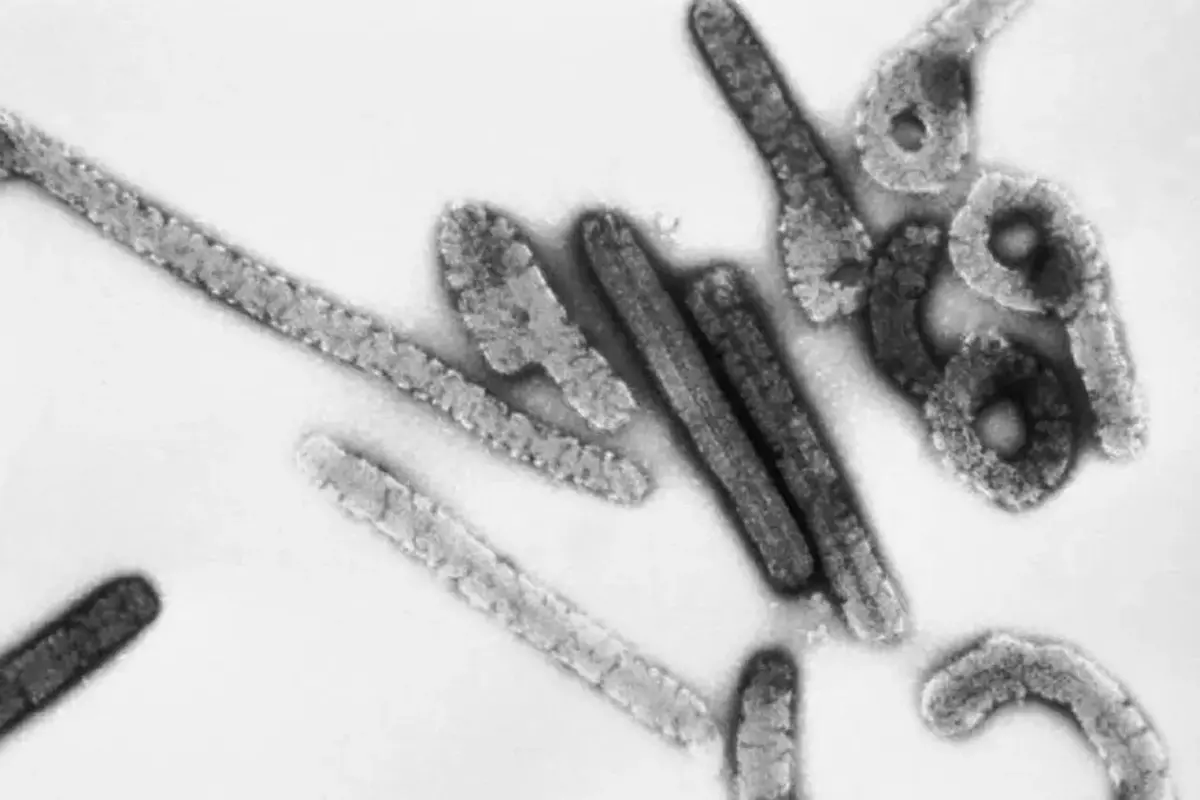
The Marburg virus sickness, which is very contagious, has now been verified in two instances in Ghana; according to a statement released by WHO on Sunday.
Two unrelated patients from Ghana’s southern Ashanti area; who later died both tested positive for the virus, prompting the announcement.
According to WHO, the patients reported diarrhoea, fever, nauseousness; and vomiting as symptoms, and more than 90 contacts are being kept under observation.
According to WHO, Marburg is a highly contagious viral hemorrhagic fever; that is related to the more well-known Ebola virus illness and has a death rate of up to 88 percent. It said, “Illness starts suddenly, with high temperature; terrible headache, and malaise.”
According to the WHO, the virus is carried from fruit bats to humans and can then be transferred; from one person to another by coming into touch with their body fluids, contaminated surfaces, or items.
The international health organisation said that containment measures were being implemented; and that additional resources will be used to address the epidemic in Ghana. WHO also cautioned that “Marburg can rapidly get out of hand; without early and effective response.”
[embedpost slug=”ghana-confirms-its-first-outbreak-of-the-deadly-marburg-virus-reports-two-deaths”]
The Marburg virus is not yet the target of any licenced vaccines or antiviral medications. However, therapy that includes oral or intravenous rehydration; and treatment of certain symptoms might increase a patient’s chances of life; according to the WHO.
To assist limit the chance of the virus spreading, the Ghana Health Service has advised the general population in Ghana; to stay away from mines and caves where fruit bats live; as well as to properly prepare any animal items before eating. The health agency said that fruit bats are the Marburg virus’s natural hosts.
Only two outbreaks have been reported in West Africa; the first being in Guinea last year. The patient in the epidemic in Guinea perished from the virus as well. Guinean health officials reported that there were no new instances.
Previous outbreaks have been documented in various countries of Africa; including South Africa, Kenya, Angola, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. More than 200 individuals died in the Angola epidemic in 2005; making it the worst.
WHO reports that nations with a higher risk of a viral outbreak; have been notified and are “on notice.”
[embedpost slug=”ghana-ali-disclosed-her-husbands-first-marriage-for-the-first-time”]